50 Years Later: TV’s Longest Ever Remote Remembered
The professional video industry's #1 source for news, trends and product and tech information. Sign up below.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
In commemoration of the 50th anniversary of the Apollo 11 moon landing this week, TV Technology is rerunning James O'Neal's series of articles from 2009 on the development of the imaging system used to transmit live broadcasts from the moon.
SEVERNA PARK, Md.—On the evening of July 20, 1969, when Neil Armstrong set foot on the moon and proclaimed that his action amounted to “one small step for man and one giant leap for mankind,” it signaled the beginning of a new era in space exploration and was viewed live by perhaps the largest television audience ever—more than half a billion people.
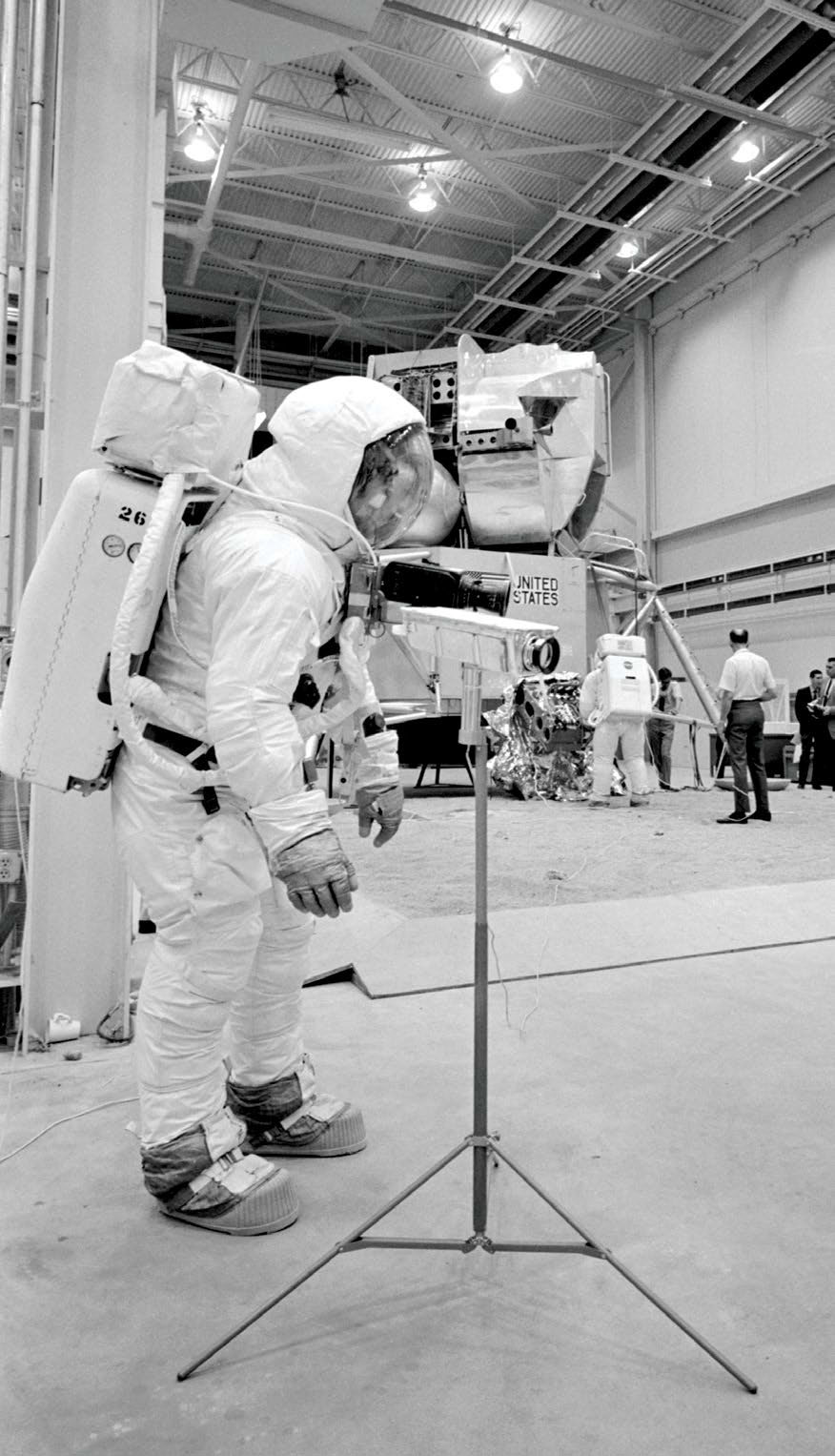

For those of us who witnessed this event live, the images coming back from the moon are etched in memory forever. The successful landing and return of the spacecraft climaxed more than a decade of the so-called “space race” with the Soviet Union, and even though the Soviets played first hand with the launch of Sputnik in 1957, America trumped it mightily with Apollo 11.
Would Armstrong’s lunar excursion have been believable without live video?
It’s conceivable that an audio broadcast might have convinced some individuals, but radio, by its very nature, plays to the theatre of the mind. Hadn’t Orson Wells one evening in 1938 convinced a large share of the CBS radio audience that Martian forces had landed in Grovers Mill, N.J., just by putting together the right mix of dialog and sound effects?
No, television had to be part of the lunar mission, or it wouldn’t have been that credible.
But how to get live video of the event back to earth and a global television audience?
The professional video industry's #1 source for news, trends and product and tech information. Sign up below.
Remember, this was the decade of the 60s when broadcast gear was big—switchers and microwave links were stuffed full of vacuum tubes, video recording was done on 2-inch tape and cameras had heads weighing hundreds of pounds and were backed by CCUs and support electronics that ate heavily into rack space.
WESTINGHOUSE GETS THE NOD
In the 1960s, the two recognized suppliers to the broadcast industry were General Electric and RCA. However, neither had, nor was planning to, make any sort of small, lightweight camera.
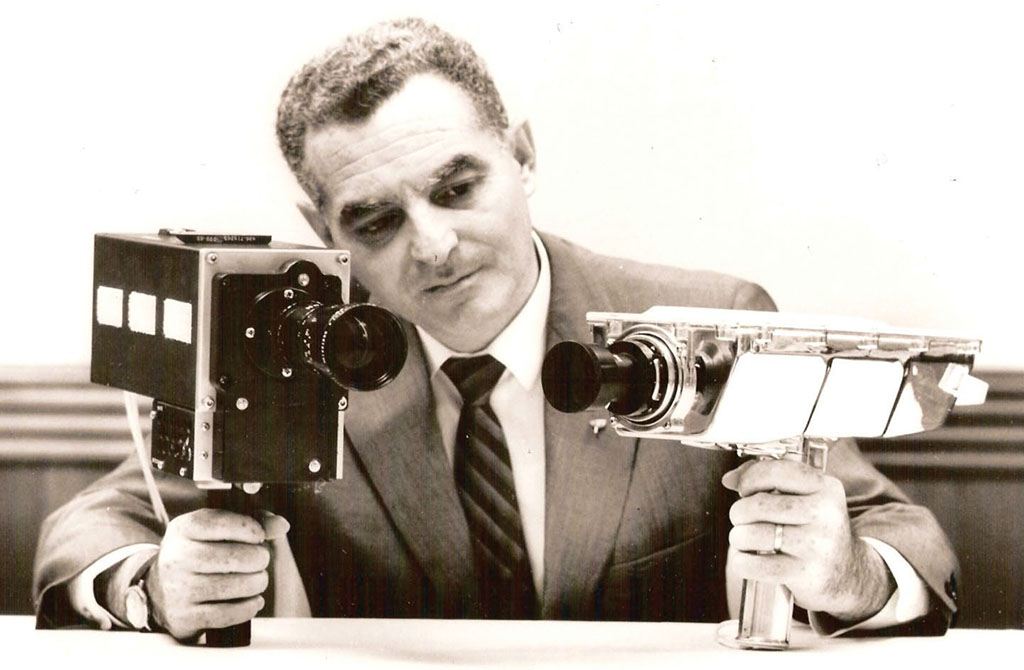

This is where Westinghouse Electric and one Stanley Lebar entered the picture.
At the time, Westinghouse had a reputation for manufacturing mainly consumer devices—electric ranges, hot dog cookers, and TV sets. To a lesser degree the company was identified as a supplier of a limited range of broadcast products such as transmitters and power tubes. But there was another side to the Pittsburgh giant—military electronics. Westinghouse supplied a lot of battle-hardened electronic gear to the Pentagon, including some small black and white television cameras for use on ships and helicopters. Westinghouse also had something that many companies didn’t at the time—a facility for fabricating custom integrated circuits solely for use by the company.
And to make the hand even more attractive, Westinghouse had created a very special television camera pickup tube; one that could run circles around conventional image orthicons and vidicons in terms of size, sensitivity, S/N and lag. This was the secondary electron conduction, or SEC, tube. It had an outstanding dynamic range and was so sensitive that, without stretching the truth too much, it could make pictures of the proverbial black cat in a coal bin at midnight.
These facts weren’t wasted on the small group of NASA officials who were promoting video from space on the Apollo missions, and in particular the planned manned lunar landing. If a compact, reliable and high performance camera were to be constructed, it would need a tube such as the SEC, along with a customized chip set to drive it.
“We had all of the building blocks that they were looking for at the time,” said Lebar, who would be tapped to head up the Westinghouse camera program for the Apollo missions. “NASA concluded that we were the only company that could do it.”
Lebar, whose career track had been in airborne radar, not video, reflected that even though the camera would be a sole source procurement, Westinghouse still had to deliver a written proposal to the government.
“We were already working on tracking sites,” he said. “And I had a trip to South America scheduled in 10 days. But we pulled a team together and put together the proposal in a week. I’d already left for Ecuador when they called me and told me to get to Houston to negotiate a contract for the camera with NASA. That was in July of 1964.”
Lebar, who now lives in the Baltimore suburb of Severna Park, Md., said that under the contract that was hammered out, Westinghouse had to initially deliver 10 camera engineering models.
And the space camera couldn’t be just reverse engineered from existing circuitry either. Other NASA specs spelled out the impossibility of using 525-line, 60-field video.
“They told us that we had only 500 kilohertz of bandwidth for video,” Lebar said. “This limited us to 320-lines and 10 frames per second with no interlace.
“Also, the camera had to have an environmental range of from plus 300 degrees to minus 250 degrees Fahrenheit. The specs covered every environmental aspect that the LEM (lunar excursion module) and moon surface would see.”
Lebar and his team soon set to work on designing the unusual camera, but found the NASA specs, especially those defining video performance to be extremely confining.
“Several managers commented up front that ‘this was a dog,’” Lebar said. “Ten frames per second and 500 kHz of bandwidth don’t make good images. We were fighting for at least an additional 250 kHz. And you have to remember that standards conversion technology was very primitive then; we had to convert this 320-line, 10 fps video to something that the networks could broadcast. RCA made an image converter to work with a camera they had—it was basically a 525 camera shooting a CRT displaying slow-scan video images. Not the best quality.”
With such a contrivance being the state-of-the-art for standards conversion, Lebar and his team knew that every fraction of a dB in camera S/N performance was precious.
“When we built the camera, we went to extreme lengths to keep the noise down to an absolute minimum,” he said. “We knew that a lot of noise would be added in the optical conversion and in relaying the video around the world from the tracking stations.”
The Westinghouse team did deliver a workable camera in time to be used on some of the Apollo missions leading up to the one now planned for July 1969; the one that would actually put a man on the surface of the moon.
However, early that year, it seemed that the camera might not be a part of that trip after all.
NOT MISSION-CRITICAL
“George Lowe, who was head of the Apollo program, called a meeting to decide if we really should fly a camera to the moon or not,” Lebar said. “It was a big meeting—all the sub-system people were there, and all of the astronauts.
“It was being argued that it [the camera] served no scientific purpose, so it shouldn’t be carried to the moon. The NASA attitude then was that it was a ‘fifth wheel.’ They termed it ‘non-mission critical.’” (This meant that no damage would result whatsoever if the camera failed or had to be jettisoned for some reason.)
“However, the old timers made it know that this was not the case—that NASA shouldn’t miss the opportunity to televise the mission.”
Lebar remembered that it was really mission commander, Neil Armstrong, who cinched the deal. Armstrong ruled the roost and stated that he wanted the camera aboard. That was that. There would be live video.
SIX PEOPLE, SIX CAMERAS
In addition to operating over a wide range of temperatures, the Apollo camera had to be special in other ways too. Lebar recalled that NASA insisted on an automatic light control system—something unheard of then in live broadcast cameras. Also there was a lot of concern about the 8 kV that the SEC tube needed. Arcing was feared to be a major concern in the high vacuum conditions encountered on the moon. Special alloys had to be developed for use in connectors exposed to vacuum conditions too.
A special group of Westinghouse employees—all women—were hand selected to assemble the cameras going aboard the spacecraft.
“We even brought in a psychiatrist to help in selection of the people used to build the cameras,” Lebar said. “We chose six top people for the job—one camera per person. This was so that one person made every decision involving construction of the camera. The women treated the cameras like they were their own children.”
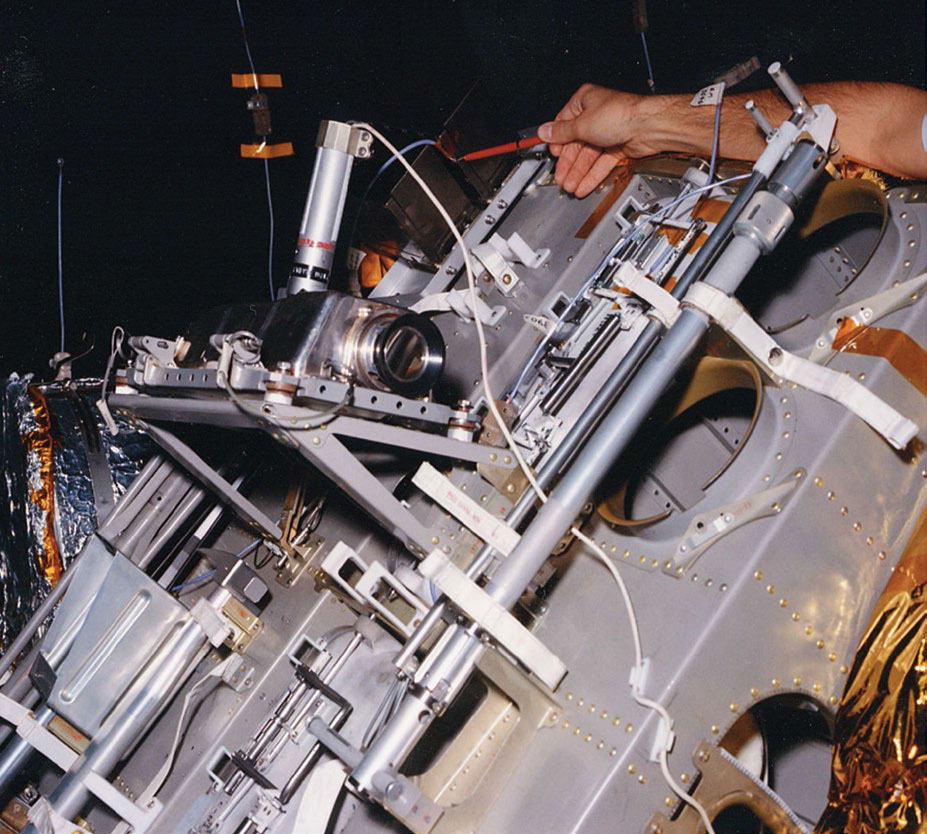
The finished cameras were inspected by three of Westinghouse’s top QC people and a government inspector.
“When it was finally time to get ready for Apollo 11, we all got very nervous,” Lebar said. “There was not going to be any backup camera inside the lander. We had some very high level NASA people at the plant at this time and they asked me if I believed that the camera would really work.”
Lebar had to admit that his answer was a bit evasive.
“I told them that my program manager had done everything possible to make it a success,” he said. “We believed that the camera would be successful, but we did worry a lot about the connectivity back on earth—the landline connections.”
Actually the situation might be painted as a bit more dire. Lebar recalled that the president of his division of Westinghouse had an independent contractor conduct a study of the potential for failure or success of Apollo’s video component. The study indicated only a 50 percent probability of everything falling into place.
“We were worried about the corporate image being on the line then,” Lebar said. “The company slogan was ‘You Can Be Sure If It’s Westinghouse.’ We really had to be sure.”
Actually, on a personal basis, there was a lot more at stake for Lebar. He’d been informed by corporate management that if the camera failed for any reason, he would be the Westinghouse employee that would have to stand in front of the cameras and reporters and explain to the world why there was no video.
“And I didn’t really want to have to do that,” Lebar said.
LIVE FROM THE MOON
The big night—July 20, 1969—found the Westinghouse team as ready and confident as possible that the camera would deliver video from space as planned. However, as with any complicated and multifaceted project, there is always the nagging uncertainty that something might not quite work out as planned.
Lebar waited out the evening in a lab at the Houston Manned Spacecraft Center or MSC (later renamed the Johnson Space Center). Video gear had been set up for monitoring the moon “remote” and he recalled his experiences after the LEM set down safely and Houston gave approval for the first moonwalk, shortly before 11 p.m. EDT.
“Suddenly this railroad train was coming at you very fast,” said Lebar. “What if this thing doesn’t work? What am I going to say? Both Westinghouse and NASA had asked me to be the point person if a failure occurred. The corporate image was on the line. It was difficult beyond all belief.”
The order was given to power up the camera, and Lebar crossed his fingers and rubbed his rabbit’s foot once more.
“The camera was on the LEM’s ‘porch’ looking out at the ladder and was in total darkness, so there was no video,” Lebar said. “Armstrong had to pull a ‘D’ ring to open the door. About two seconds after the turn-on command was given, I saw a sync pulse on the monitor and thought ‘it looks like it’s going to work.’
“All the tension and agony drained out of me when the door was opened and I saw video and realized that we were successful. Then I was in seventh heaven.”
However, the video that was making its way across 239,000 miles of space and several thousand more of terrestrial linkage was far from perfect.
“The image was bad, very dark,” said Lebar. “Someone at the [Goldstone, Calif.] tracking station was adjusting the [scan] converter. The image actually went negative for a while.”
Lebar found out later that the Goldstone video technician was new to the job and had never operated the optical converter before that evening.
“He just turned every knob he could and then froze up,” said Lebar.
(Actually the first images reaching terrestrial television viewers were inverted top-to-bottom, as the camera was initially resting upside down. Its top plate was the only flat surface and this was the way the camera rested until Armstrong removed it and began to carry it by the pole-type handle on its underside. The inversion was correctible by flipping a switch on the converter.)
“Someone said that they were getting a better picture from the tracking station in Parkes tracking station in Australia [actually a radio telescope installation],” Lebar said. “We switched over to Parkes and never went back to Goldstone.”
Due to the primitive image conversion technology, contrast was blocked up and a lot of noise was added to the picture; so much so that the images took on a ghostly, ethereal look—quite different from the video being pumped out from the ABC, CBS and NBC studios in New York that evening. However, this seemed to fit correctly into the scheme of things.
“The comment was made then that if the video had looked like the live television everyone was used to, no one would have believed that it was coming from the moon,” said Lebar.
Now that he, Westinghouse, NASA, and the world at large was assured that the $1 million camera was actually working as planned, Lebar took time out to ponder what had been going through his mind that evening.
“I had very mixed emotions,” he said. “Worry, success when the sync pulse came up, then distress when the image wasn’t that good, then happiness when the switch to Parkes was made.”
Even after 40 years, Lebar says that he still hasn’t been able to completely sort out his emotions from that very special evening.
“I just know that I never want to go through this again.”
Asked if he had made any special comments or proclamations about the event at the time, Lebar revealed that he had summed up the moment very simply.
“I just said that I thought it was great.”
What else does Lebar remember from that evening of evenings?
“There was an all-night party at the King’s Inn motel near the MSC,” he said. “Westinghouse rented several rooms there on a yearly basis and the celebration was held in the motel’s restaurant. They served champagne all night long. At seven in the morning they fed breakfast to anyone still standing.”
See also:
Equipping Apollo for Color Television
James E. O’Neal has more than 50 years of experience in the broadcast arena, serving for nearly 37 years as a television broadcast engineer and, following his retirement from that field in 2005, moving into journalism as technology editor for TV Technology for almost the next decade. He continues to provide content for this publication, as well as sister publication Radio World, and others. He authored the chapter on HF shortwave radio for the 11th Edition of the NAB Engineering Handbook, and serves as contributing editor of the IEEE’s Broadcast Technology publication, and as associate editor of the SMPTE Motion Imaging Journal. He is a SMPTE Life Fellow, and a member of the SBE and Life Senior Member of the IEEE.

